---
id: "202203101"
date: "2022/03/10 20:15"
title: "Q39 组合总和(combination-sum)"
tags: ["java", "leetcode", "dfs"]
index_img: https://qiniupic.fleyx.com/blog/202203101631050.jpg?imageView2/2/w/200
banner_img: https://qiniupic.fleyx.com/blog/202203101631050.jpg
categories:
- "算法"
- "leetcode刷题"
---
202203101
## 解析思路
leetcode 中等难度,题目描述[点击这里](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/)。
标准的回溯类题目,对于回溯类题目,通常都是要穷举所有的情况,然后判断那些情况是符合题目要求的。
然后穷举通常是通过`深度优先搜索(dfs)`来实现的,我们可以先将结果展开成一棵树,然后再根据这棵树来写代码,就比较好理解,如下图:
以[2,3,5],8 为例:
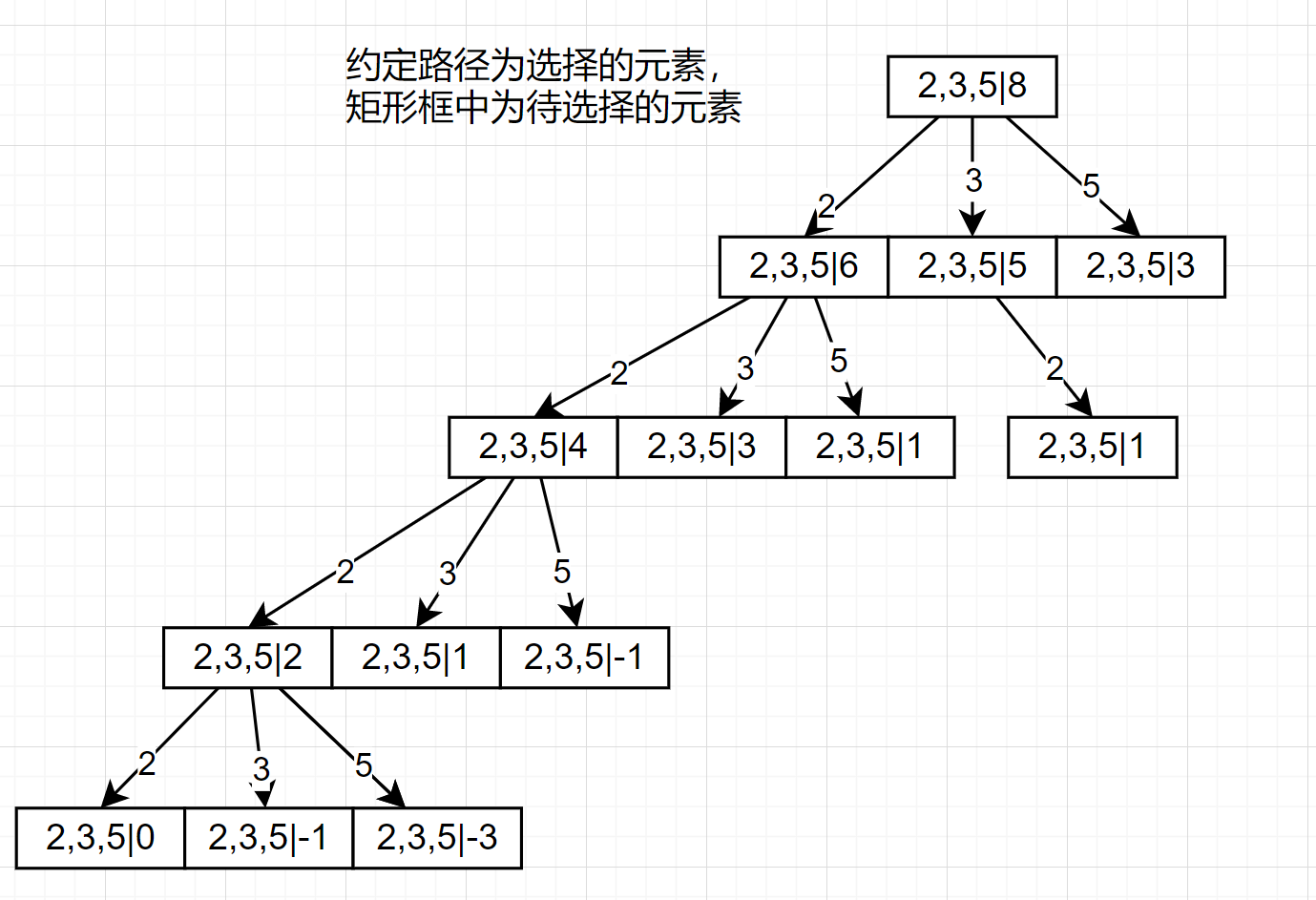
上图只对最左边的路径进行了完全展开(全部展开太麻烦了)
总的来说回溯就是不断的进行尝试,如果尝试到最后发现不满足要求那就换一个路径继续尝试,属于暴力算法。因此此类题目的数据规模通常会限制的比较小。
另外通常还能根据题目的要求来做剪枝操作,减少一些不必要的运算。
比如本题可以先将数组排序,当选择的某个数已经大于目标值时,就没必须选择这个数的下一个数继续尝试了。
## 代码
```java
public class Q39 {
public List> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
//排序
Arrays.sort(candidates);
dfs(candidates, target, 0, new Stack<>(), res);
return res;
}
private void dfs(int[] candidates, int target, int index, Stack temp, List> res) {
if (target == 0) {
//说明找到一个结果序列
res.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (candidates[i] > target) {
//前面已经排序过,所以在这里可以进行剪枝操作,如果candidates[index]都小于target了,那就不需要比较后面的了,肯定不满足要求
return;
}
temp.push(candidates[i]);
//注意这里,为了让结果集不重复,选择重复元素时只能对当前元素进行重复选择,不能重复选择之前的元素。所以递归的index为i,不是0
dfs(candidates, target - candidates[i], i, temp, res);
temp.pop();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Q39().combinationSum(new int[]{2, 3, 5}, 8).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
```